As soon as the benchmarks hit the web, the GeForce RTX 20 series graphics cards has been bombarded with mixed comments regarding to its performance and performance over its predecessor, the GeForce GTX 10 series graphics cards. While many are getting mixed bag of results (including ourselves) on the comparison on raw performance, power consumption, heat output, etc, it doesn’t really shows what these cards are capable of with the advertised RT and Tensor cores.

We recently attended the NVIDIA Regional Media Briefing in Bangkok, Thailand to take a deeper look into what NVIDIA has to offer with its latest GeForce RTX 20 series graphics cards. As we’ve already seen the raw performance of the RTX 20 series graphics cards, what’s coming next is the technology itself – how will these dedicated RT and tensor cores benefit us, the end-users on the long run.
As Microsoft has yet to release its Windows 10 October 2018 update, pretty much all of the reviews you’ve seen to date doesn’t really shows what can the Tensor and RT core do due to the absent of Windows Machine Learning and DirectX Ray Tracing.
More Than Just Raw Performance
Having large amount of CUDA cores for that extra beefy performance isn’t the only thing the Turing architecture based GPU got. While we have yet to see how it performs in game, here’s a basic idea on how things works for NVIDIA’s newly added features to its consumer graphics; RT cores handling the workload on real-time Ray Tracing and Tensor cores on large matrix operations on AI.

With that being said, RTX isn’t just about real-time Ray Tracing alone. Real-time Ray Tracing is only a part of the feature that falls under the big umbrella of RTX, along side other features that harness the power of AI i.e DLSS, advanced shading method, AI content creation and touch up.
Real-time Ray Tracing
Let’s start off with the much hyped real-time Ray Tracing, mind you – ‘Real-Time’ is the main focus here. Since NVIDIA announced the GeForce RTX graphics cards, we’ve seen quite a lot of comments from the community regarding to this feature, both positive and negative. We believe that many of you are aware that Ray Tracing has been around for a very long time, but having it to run on real-time? Not really.
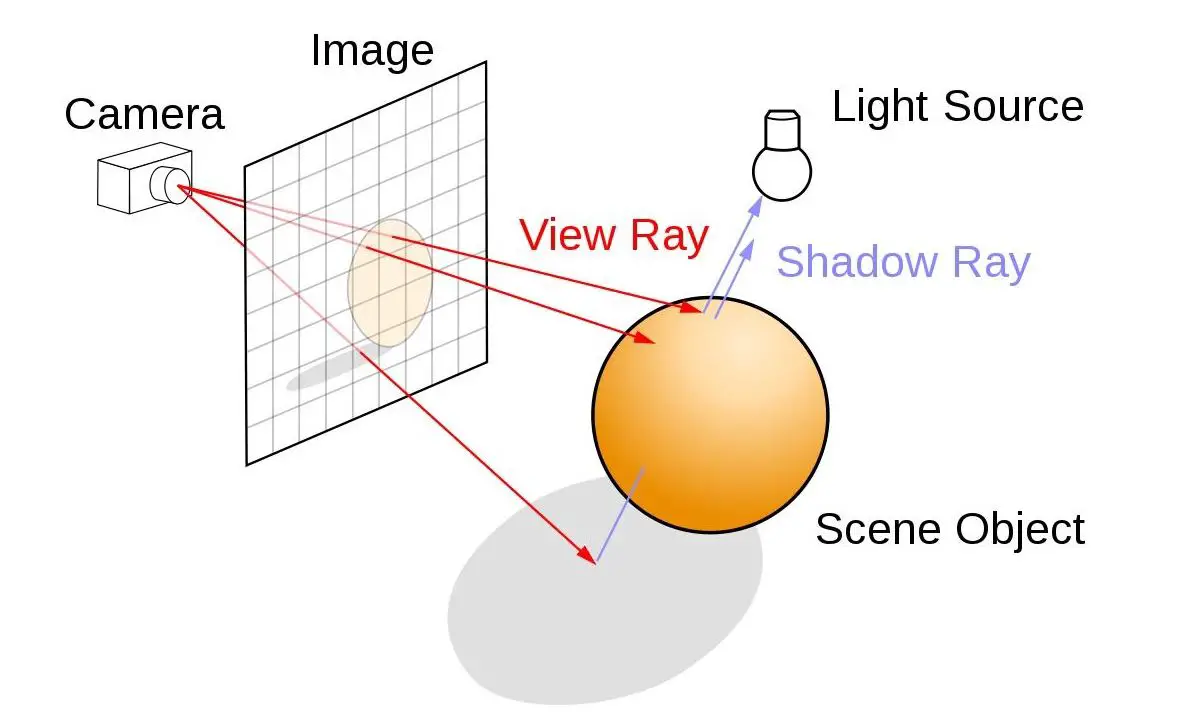
To achieve physically accurate lighting, or how light behave in real life is not an easy task. Reflections on object surface, refractions through transparent or translucent object, indirect lighting from other light source, casting shadows and silhouette of affected objects is part of what’s happening in Ray Tracing acceleration, which requires a lot of calculations.
Let’s have a quick look on how things work:
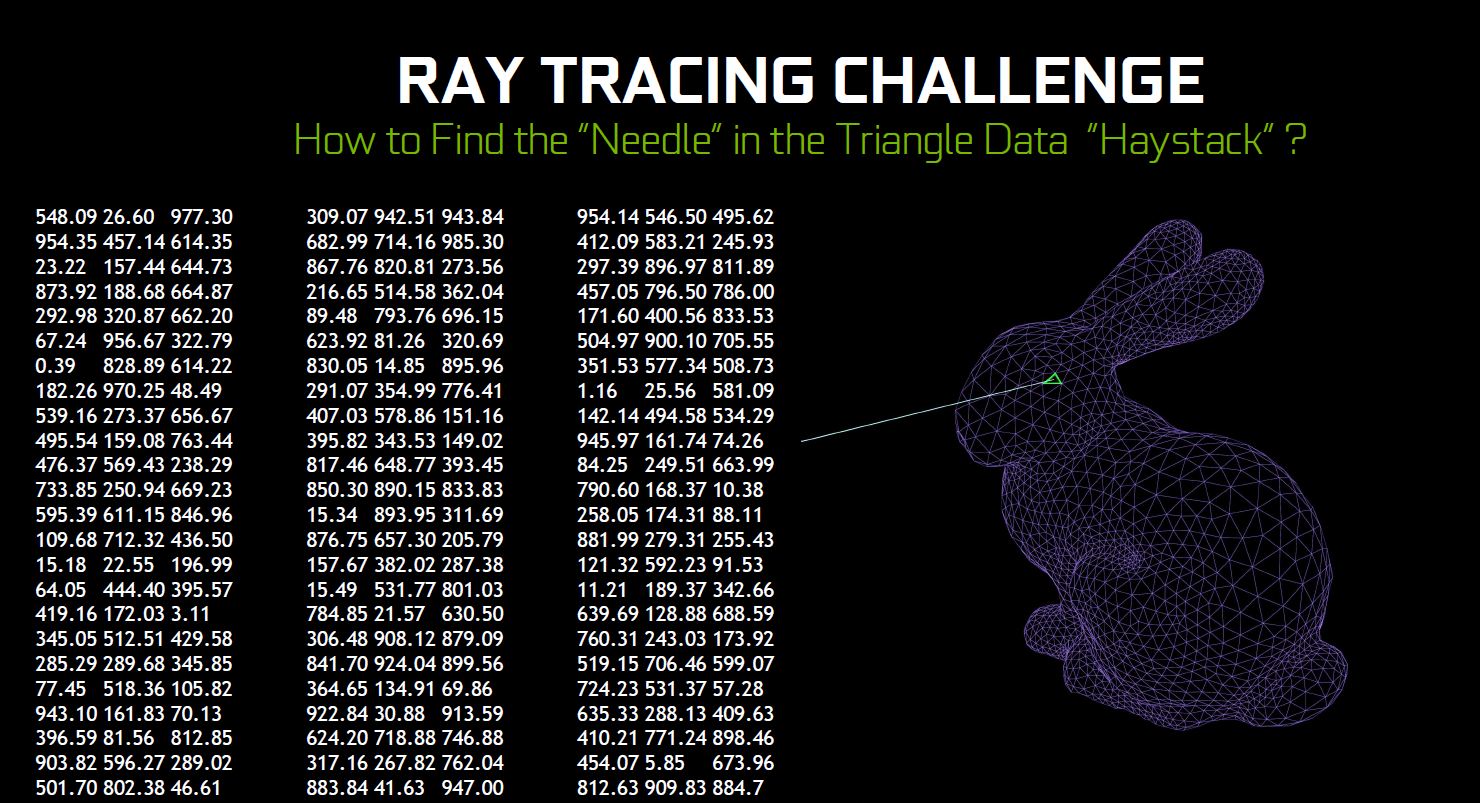
A 3D object are made up of a lot of tiny triangles that has different characteristics of its own which blocks, reflects, allow or partially allow light to pass through it. In Ray Tracing, you are basically tracing the light from the camera back to the source of light. As light travels through the scene, it hits these small triangle on the objects available in the scene and bounces off or passes through it, depending on the type of material and surface of the object.
Data for each and every of these ray of light will then be used to determine how the object should look like in real life to create a photo-realistic image based on the brightness intensity of the surface, the amount of light allowed to pass through, the shadow to cast, etc.
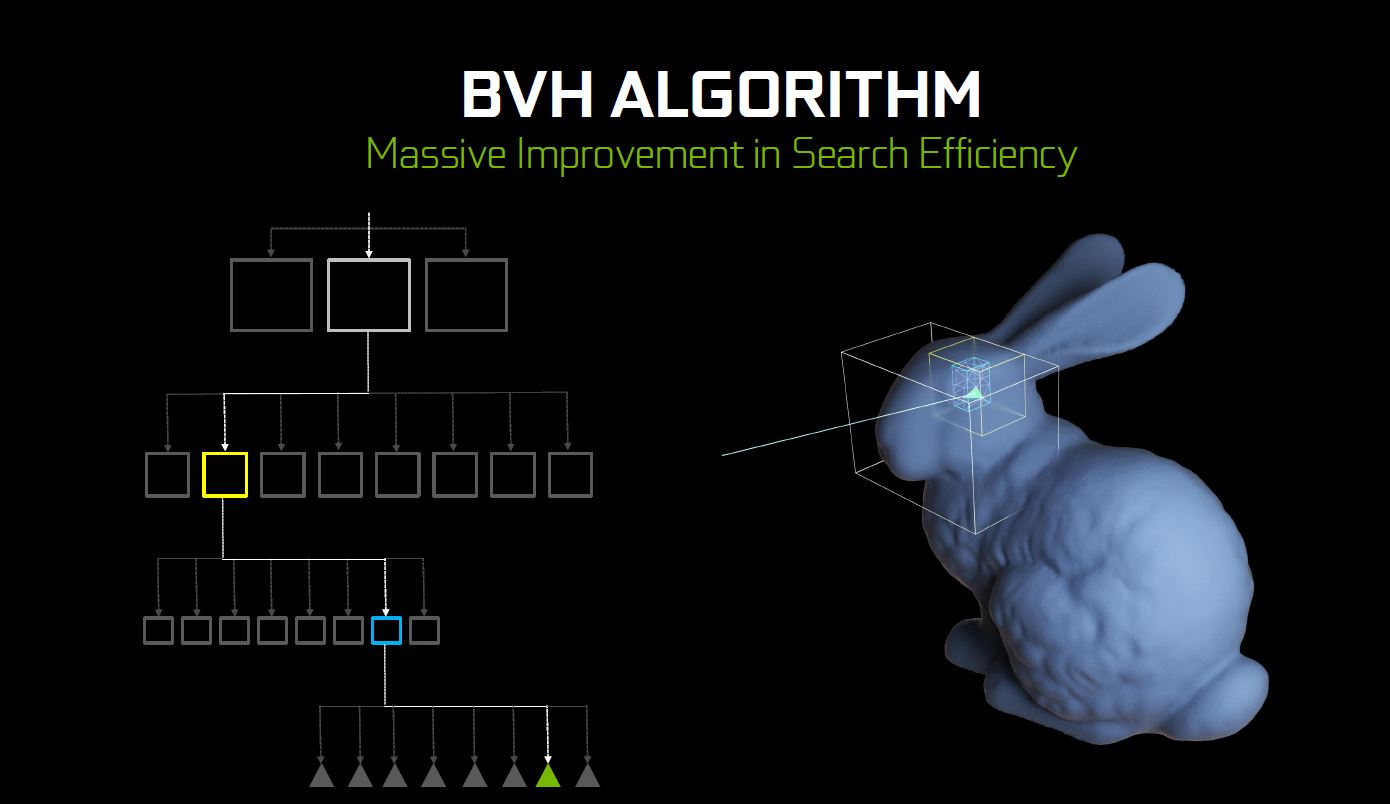
Bounding Volume Hierarchy (BVH) is the method used here to determine if the ray of light has actually intersects with any of the the triangles in a region, somewhat similar to the Binary Search Tree (BST) if you’re into accelerating data searching with data structure. Once that region is determined, you can pretty much ignore the rest and traverse to the smaller region of the node to get that exact triangle that intersects with the light. That’s just for a single triangle alone – try to imagine amount of calculations required to accurately determine each and every of these triangles in just one scene.
By having a hardware that is dedicated for this calculation, real-time Ray Tracing can be achieved with very minimal compromise to the overall performance.
What’s Up With Tensor Cores?
Now that we know what does the RT cores does, let’s move on with the Tensor cores. This involves Deep Learning AI, something which NVIDIA has been working on for years.
Deep Learning involves long hours, or maybe years to train, learning from mistakes overtime to achieve the supposed result accurately for a certain task. Upscaling a low res image to high res, determine the accurate next frame and insert it in between frames to create a smoother slow motion video, content aware fill feature for image touch up are some of the features that can be achieved with Deep Learning, and the Tensor cores is what helps to accelerate this complex operation.
Before we dive into NVIDIA DLSS, here’s a quick demo on DLSS by John Gillooly, Tech Marketing of NVIDIA:
The NVIDIA DLSS, Deep Learning Super Sampling is part of what it is capable of. Extremely high res images are fed to the neural network where it is trained to generate the next frame based on prediction, trial and error until an accurate version is produced.
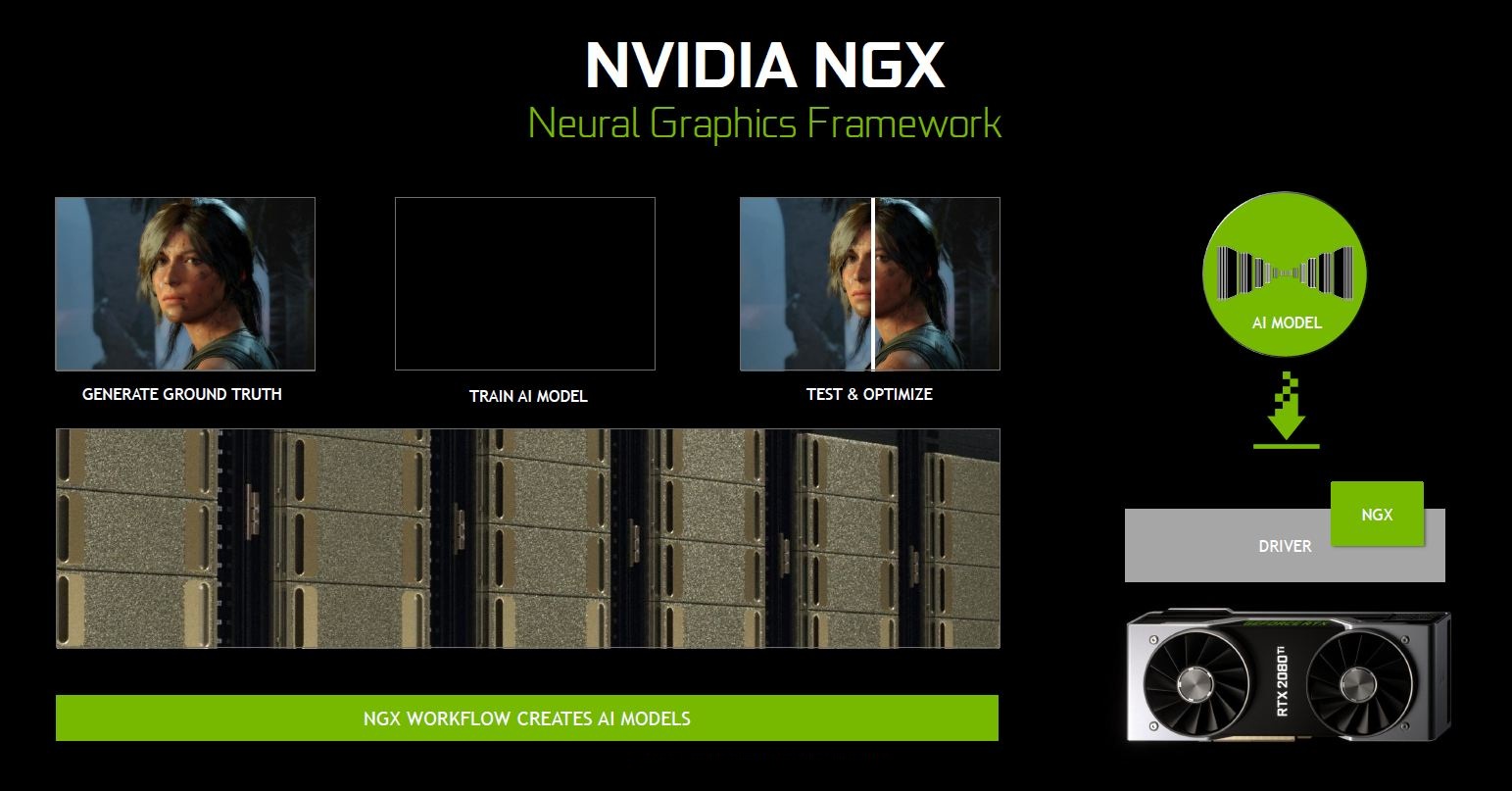
This greatly benefits gamers who enjoy every single detail of the game that they’re playing, as all these high res images has already been pre-processed to achieve the best possible quality with very minimal impact to the performance. This is when the NVIDIA NGX comes to play. So, how does the NGX works?
It will first generate a ground truth – the definition of the perfect image, followed by training the AI model by continuously generating a predicted output until it’s the closest to ground truth. Once the AI model has been tested and optimized, it is made available to the end-users via driver update, in case if they decide to enhance the image quality of the games they’re playing. Of course, it will only be available if the game developer decide to provide NVIDIA with all the necessary data that is required for the training.
Advanced Shading
Apart from the details, a properly done shading too plays an important role in producing a realistic scene. As you get more objects appearing in a scene, there’s a whole lot more shading that has to be done and again, more processing power required to achieve that.
Instead of drawing everything in detail and start shading each and every last of the surface of each object drawn, NVIDIA has a different approach to handle this through the use of mesh shaders, a new programmable geometric shading pipeline available to the Turing architecture.
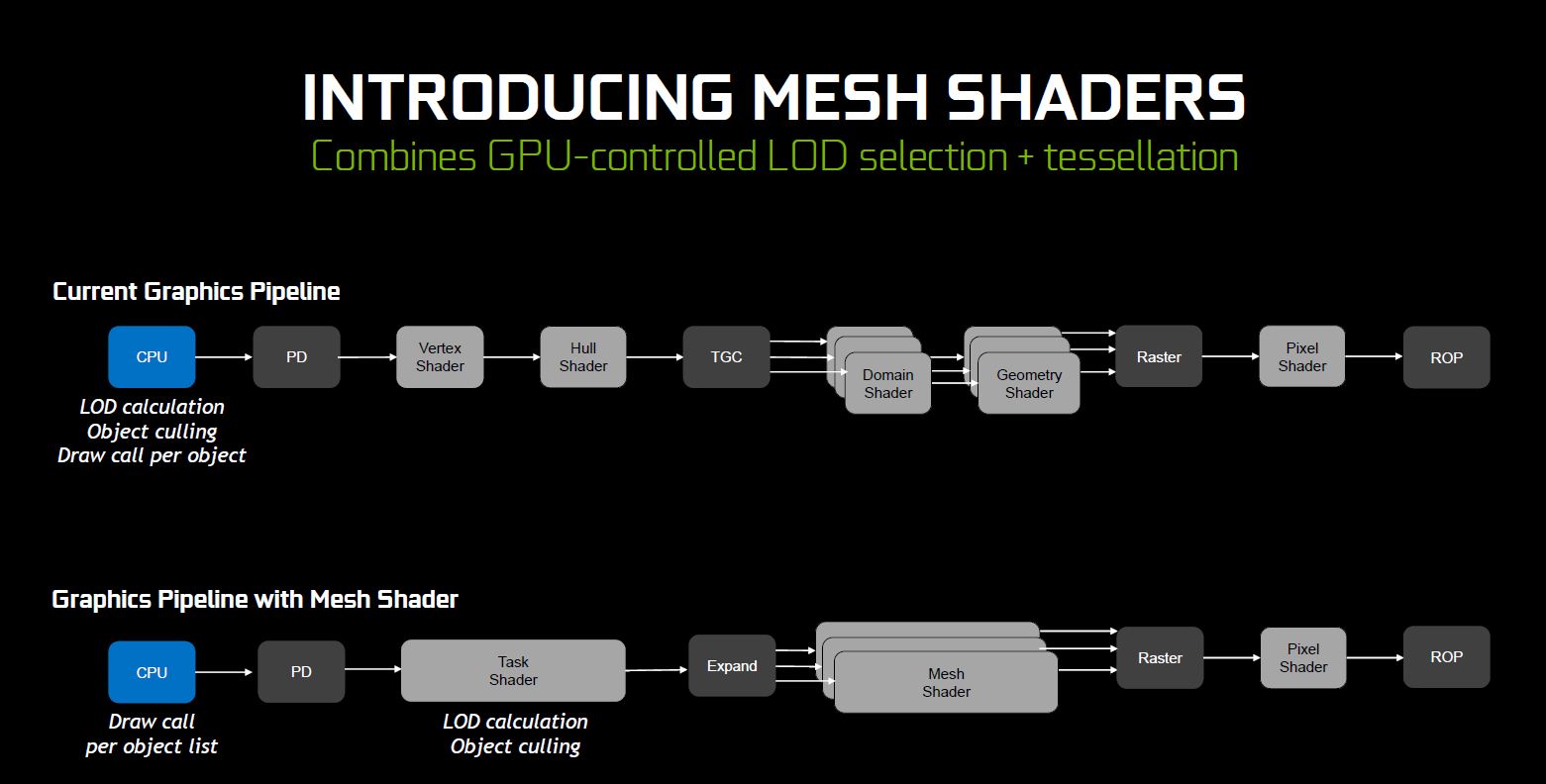
It acts similar to how we perceive things in real life by segmenting objects and its surface to different level based on the distance, followed by the level of detail to be drawn onto it. Take this as an example, if you look at a tree from a distance, you’ll only see the shape of the tree as a whole. As you move closer to it, you’ll see more details i.e surface and texture of the tree trunk, leaf grain, etc.

Lower overhead can be achieved through this method by shading different level of segments selectively based on the depth data of a rendered scene. This allow better performance while preserving the level of details for closer segments of a scene.
Other than mesh shading, there’s also a similar approach known as the variable rate shading that selectively shades segments that requires more shading than the rest.
Here’s a demonstration of mesh shading as well.
There’s More To Come

What we’ve mentioned above is only a tiny part of what the Turing architecture GPU is capable of. There’s a lot more features that we have yet to see, especially on other possibilities that can be achieved through Deep Learning.
There’s a lot of potential that has yet to be explored the new GeForce RTX 20 series cards, but you’ll have to at least wait for the upcoming Windows 10 October 2018 update that comes with Windows Machine Learning and DirectX Ray Tracing.
Before we end this article, here’s the full presentation done by Jeff Yen, Director of Technical Marketing, APAC at NVIDIA – in case if you want to know what’s going on during the media briefing:




















Comments are closed.